ID Codes
ID Codes

| Index | Rear Axle | Old ID Codes |
New ID Codes |
Engine Codes | Abbrevs | Links |
Email |
||

These tables look best if the browser is made as wide as possible.
Jump down to A1 Sedan
Jump down to G1 Truck
Jump down to AA, AB, AC Sedans
Jump down to WWII Trucks
Jump down to SA Sedan
Jump down to SB Truck
Jump down to BM Truck
Jump down to SF Sedan
Jump down to Publica Sedan
 |
 |
|
| A1 Sedan | ||
 |
 |
Toyota's first vehicle was the A1 sedan, with the first protoype being made in May 1935.
Its body was a copy of the Chrysler Airflow, the 3389cc engine was copied from a Chevrolet
and the chassis was copied from a Ford.
Parts were deliberately designed to be interchangeable with parts used on American made vehicles.
After a blessing ceremony in the factory courtyard, Kiichiro Toyoda drove it alone to his father's grave
and showed it to his father (his father, Sakichi Toyoda, had given him the money on his deathbed to start a car factory).
Only 3 prototypes were made.
 |
 |
|
| G1 Truck | ||
 |
 |
The economic climate wasn't right yet for a domestic car but it was right for a domestic truck.
So the A1 sedan was temorarily held back while the G1 truck was developed for production.
The G1 truck used the same basic chassis with the same engine moved forward.
A simple cab was made with a wooden bed on the back.
The first G1 protoype was made on 25th August 1935, shown to the public
on 21st November 1935 and the model released for sale 2 weeks later.
This was just in time to meet the government deadline for licensing motor vehicle producers.

Early units broke down a lot, so customers were carefully choosen for loyalty.
Aftermarket sale support was so strong that entire trucks were often replaced without question.
Development and production engineers were loaned to dealers so that repairs could be done
and so that the engineers could learn about what needed to be changed in production.
 |
 |
|
| AA, AB, AC Sedans | ||
 |
 |
Kiichiro returned to the A1 sedan and decide to develop it further.
Public reaction to the A1 was mixed, so he redesigned the body.
He wasn't sure if people would prefer a closed sedan or a phantom cabriolet, so he made both.
The sedan was called the AA and the cabriolet was called the AB.
They were mostly the same except the AB had no upper bodywork, a fold down front windscreen, rear opening rear doors (AA had suicide rear doors) and the rear seats were set further back.
They both used the 3389cc, OHV, in-line, 6 cylinder A engine.
Both were announced in Nov 1935.
The ABR was the AB as made for the Japanese army.



A total of 1404 AA units were made before the AC took over from the AA in March 1943.
The AB was discontinued.
A combined total of 353 AB and ABR units were made (most were the ABR).
Pictures copied from gazoo.com.
Toyota wanted to restore a model AA for its 50th birthday in 1987.
Unfortunately they could not find one - so they built one from the original plans.
It was harder than they thought because the plans were inaccurate and had pieces missing.
Some pieces were found in unusual places - like drawn on cloth attached to a board serving as the roof of an old World War II bomb shelter.

1987 model AA chassis.
| Country | Dates | Code | Engine | Body | Gearbox | Diff | Grade | PS/rpm | kgm/rpm | CR | Front track |
Rear track |
kg | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
3609- | AA | A | 4DS | DX | 65/3000 | 19.4/1800 | 1600 | ||||||||
 |
3609- | AB | A | 4DC | DX | 65/3000 | 19.4/1800 | 1600 | ||||||||
 |
4303- | AC | 4DS | 75/3000 | 21.6/1600 | 1825 | ||||||||||
 |
 |
|
| WWII trucks | ||
 |
 |

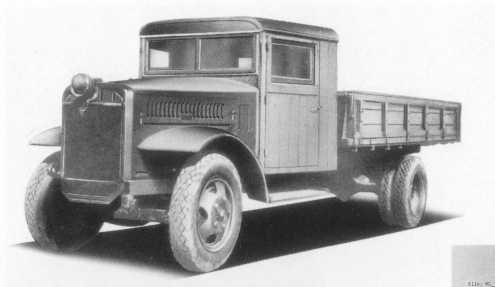
Low demand for cars combined with strict rationing of steel, rubber
and fuel meant that trucks were concentrated on during wartime.
These were very basic machines made in times of great trouble.
Supplies were so low that often trucks were made with just a single,
central headlight and only rear brakes.
 |
 |
|
| SA Sedan | ||
 |
 |
SA info copied from Toyota Museum.
995cc side valve in-line 4 cylinder.
Backbone frame, 4 wheel independent suspension.
Only 215 made.
Public input resulted in the name "Toyopet".

| Country | Dates | Code | Engine | Body | Gearbox | Diff | Grade | PS/rpm | kgm/rpm | CR | Front track |
Rear track |
kg | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
4701-52xx | SA | 2DS | 3H | 27/4000 | 1170 | ||||||||||
 |
 |
|
| SB Truck | ||
 |
 |
Introduced in 1947 a few months after the SA sedan, the SB was a small truck.
It used a conventional 2 door cab on a conventional chassis, with the SA's 995cc engine.
Many owners converted it into a 4 door sedan or 4 door wagon.

The SB was later refined into the SG small truck.
In 1955 this was further refined as the SKB.
A public competition for naming the SKB was won with "Toyoace".
 |
 |
|
| BM Truck | ||
 |
 |
Introduced in 1947, the BM was a large truck to complement the much smaller SB truck.
The BM was later refined into the BX and FX trucks.

Numerous buses and trucks followed but I will concentrate on passenger cars.
 |
 |
|
| SD Sedan | ||
 |
 |
Introduced in 1949, the SD was designed for the taxi market.


 |
 |
|
| SF Sedan | ||
 |
 |

Introduced in 1951, the SF was designed for the taxi market.
Taxis often broke on Japan's poor roads, so Kiichiro Toyoda put a car body on the SB truck chassis.
It was strong but opinion was that it was slow and looked like a baby carriage with an engine.
In September 1953, the SF (now know as the Toyopet Super) became beloved by the taxi market
after it got a facelift, a bigger 1500cc engine and a big reduction in price.
The Crown was designed to replace the Super in 1955 but Toyota wasn't sure if its independant front
suspension and its suicide type rear doors were too radical for the taxi market to bear.
So the Super was updated, renamed the Master (later Masterline) and sold alongside the Crown.
The Crown eventually took over but the Master's body panels continued in cutdown form as the ST10 and PT10 Corona in 1957.
 Toyopet Crown RS
Toyopet Crown RS
 Toyopet Master RR
Toyopet Master RR
 Toyopet Corona ST10
Toyopet Corona ST10
 |
 |
|
| Publica | ||
 |
 |
The Publica was released in June 1961.
Originally it was meant to be a cheap front wheel drive made in a joint venture with Ford.
Ford pulled out of the deal, so Toyota continued with it in rear wheel drive form.
It was designed to be small, cheap, economical and hence plain.
Unfotunately, Japan's working class had moved upscale faster than Toyota
had thought it would and they thought it too plain.
Toyota's response was to make a more upscale version called the Publica Deluxe.
The Publica Deluxe sold better than the cheaper Publica but this was still only moderately successful.
Toyota's true answer to the small car was the very successful Corolla in 1965.

The Publica name was the result of yet another public competition
and stood for Public Car - pretty close to the name Volkswagen (folk's wagon or people's car).
Later versions of the Publica were renamed as the Starlet.
Last updated 27 Dec 2007